Farming on exoplanets presents a fascinating intersection of agriculture and space exploration, raising questions about how humanity might sustain itself beyond Earth. As we venture into the cosmos, the need for sustainable food production systems becomes increasingly critical. This article explores the theoretical frameworks and technologies that could enable farming on exoplanets, examining the challenges and potential solutions that lie ahead.
The Challenges of Exoplanetary Agriculture
Farming on exoplanets is fraught with challenges that stem from the unique environmental conditions found on these distant worlds. Unlike Earth, exoplanets may have extreme temperatures, varying atmospheric compositions, and different gravitational forces, all of which can significantly impact agricultural practices.
1. Environmental Conditions
One of the primary challenges of farming on exoplanets is adapting to their environmental conditions. For instance, planets located in the habitable zone of their stars may have suitable temperatures for liquid water, but other factors such as soil composition, radiation levels, and atmospheric pressure can vary widely.
- Temperature Extremes: Many exoplanets experience extreme temperature fluctuations, which can hinder plant growth. Developing crops that can withstand these conditions will be essential.
- Soil Composition: The soil on exoplanets may lack the necessary nutrients for traditional crops. Understanding the mineral content and potential for soil amendment will be crucial.
- Radiation Exposure: Higher levels of cosmic radiation on some exoplanets could damage plant cells. Protective measures, such as underground farming or radiation-shielded habitats, may be necessary.
2. Water Availability
Water is a fundamental requirement for agriculture, and its availability on exoplanets is a significant concern. While some exoplanets may have water in the form of ice or vapor, extracting and utilizing it for farming will pose logistical challenges.
- Water Extraction Technologies: Innovative technologies will be needed to extract water from the environment, whether it be from ice deposits or atmospheric moisture.
- Water Recycling Systems: Closed-loop water systems will be essential to minimize waste and ensure a sustainable supply for crops.
3. Gravity and Its Effects
The gravitational forces on exoplanets can differ significantly from those on Earth, affecting plant growth and development. Research into how different gravity levels influence root systems, nutrient uptake, and overall plant health is necessary.
- Root Development: In lower gravity environments, plants may struggle to establish strong root systems, which could impact their stability and nutrient absorption.
- Growth Patterns: Understanding how plants adapt their growth patterns in varying gravitational conditions will be crucial for successful farming.
Potential Solutions for Exoplanetary Farming
Despite the challenges, several potential solutions and technologies could facilitate farming on exoplanets. These innovations may draw from advancements in terrestrial agriculture, biotechnology, and space exploration.
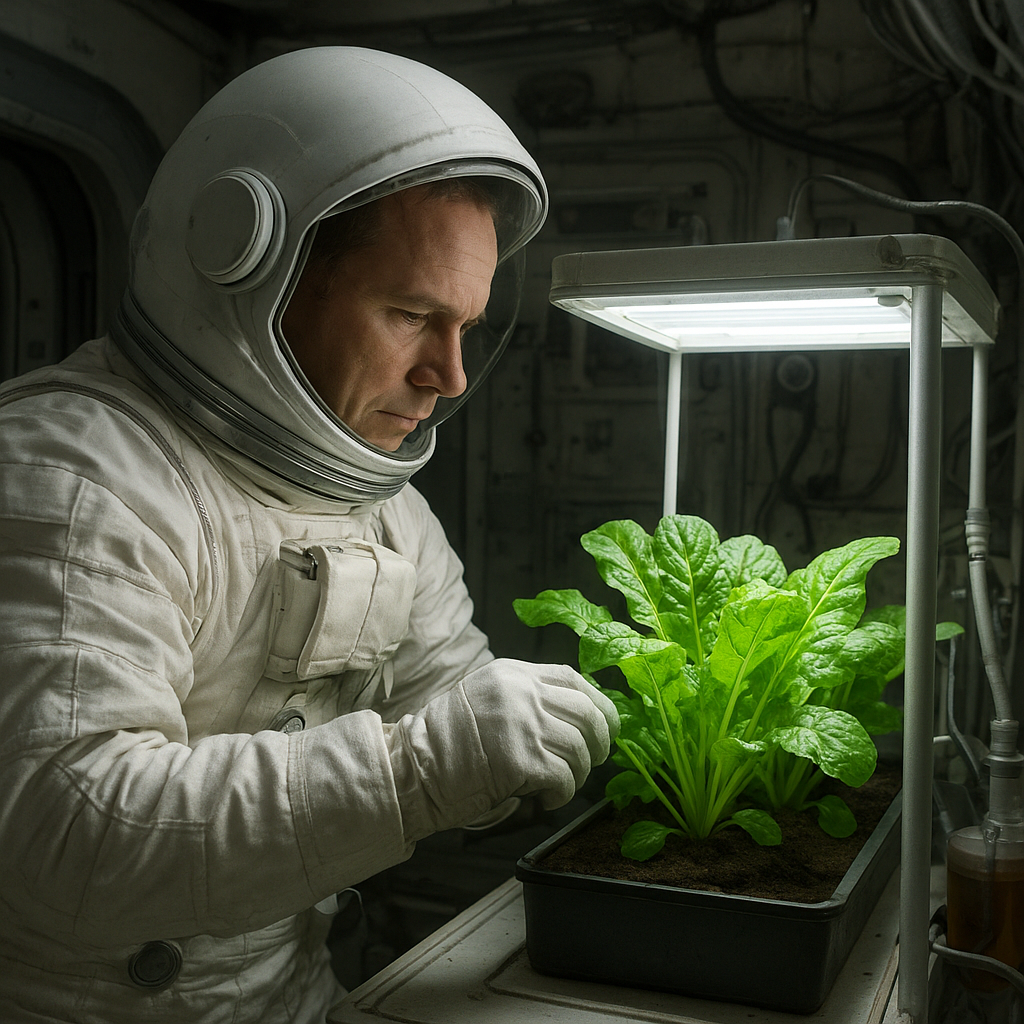
1. Hydroponics and Aeroponics
Hydroponics and aeroponics are soil-less farming techniques that could be particularly advantageous for exoplanetary agriculture. These methods allow for efficient nutrient delivery and water usage, making them ideal for environments where traditional soil farming is impractical.
- Hydroponics: This method involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions, which can be easily controlled and monitored.
- Aeroponics: In this system, plants are suspended in air and misted with nutrient solutions, promoting rapid growth and reducing water usage.
2. Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering holds the potential to create crops that are specifically tailored to thrive in the harsh conditions of exoplanets. By modifying plant genomes, scientists can enhance traits such as drought resistance, nutrient efficiency, and resilience to radiation.
- CRISPR Technology: The CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing tool allows for precise modifications to plant DNA, enabling the development of crops that can withstand extreme conditions.
- Bioengineering for Nutrient Uptake: Engineering plants to improve their ability to absorb nutrients from non-traditional soils could enhance their viability on exoplanets.
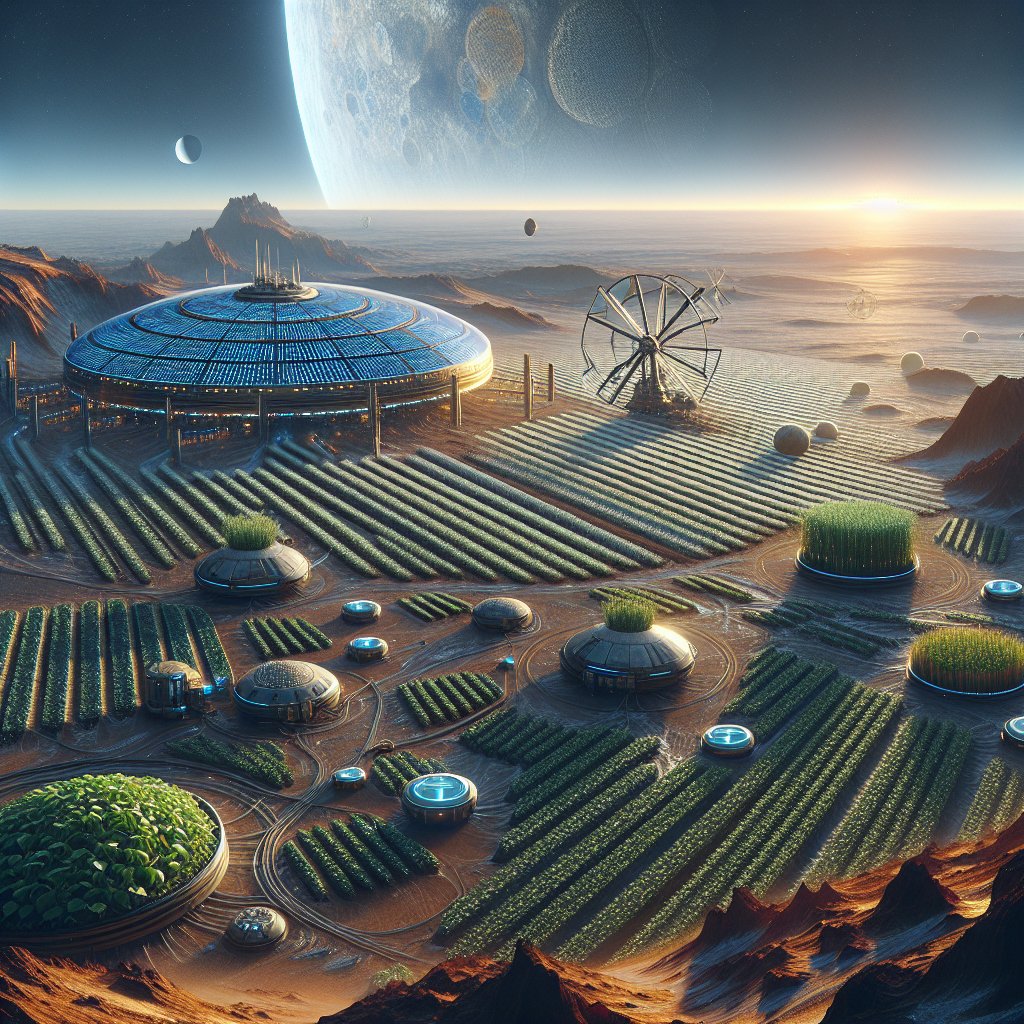
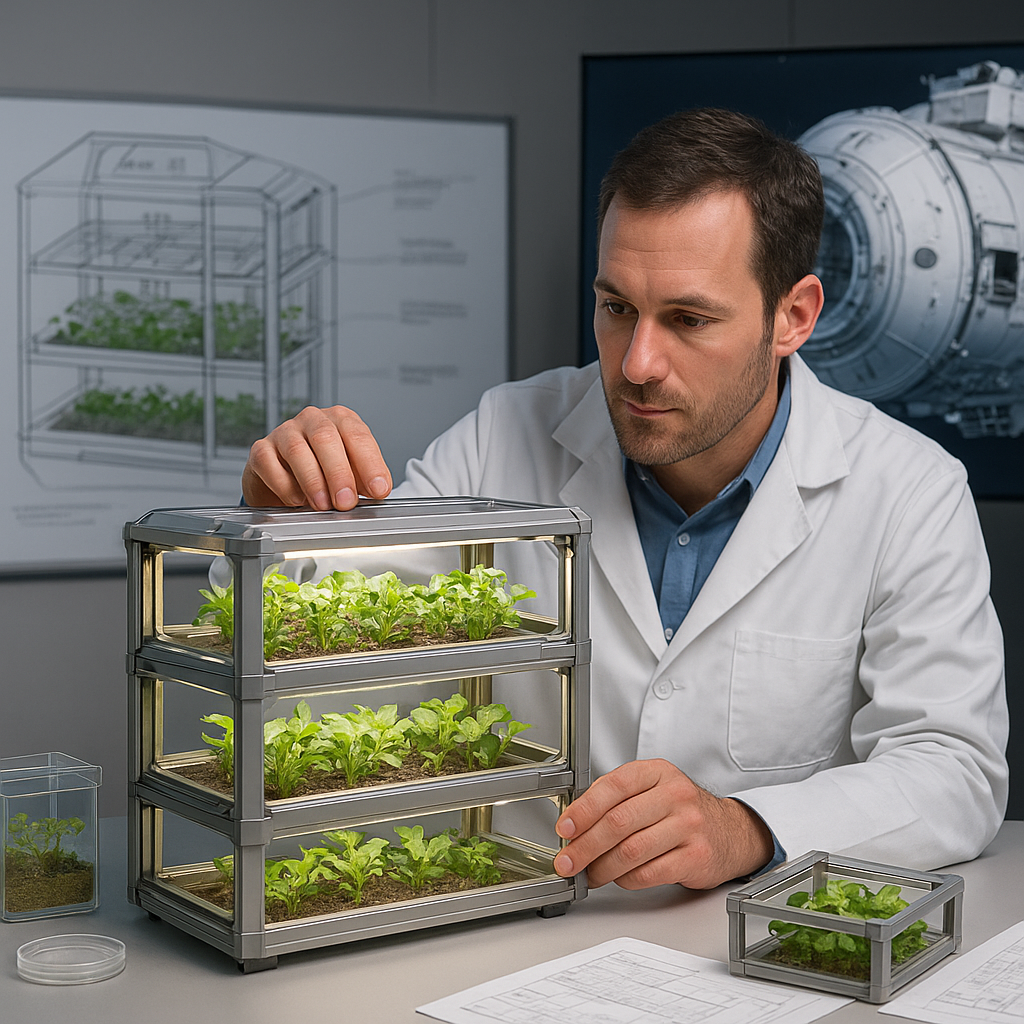
3. Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA)
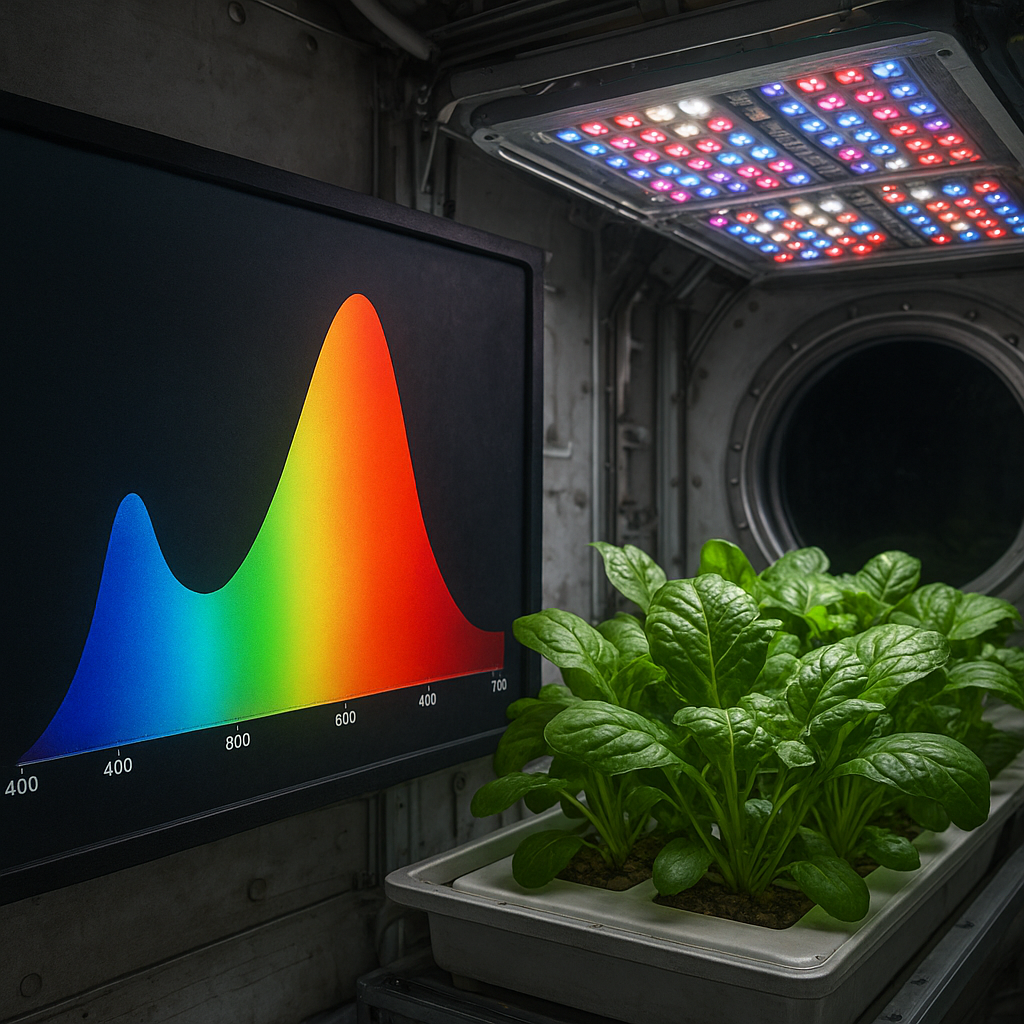
Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) involves creating optimized growing conditions for plants, often using technology to regulate temperature, humidity, light, and nutrient levels. This approach could be particularly useful in exoplanetary settings where external conditions are unpredictable.
- Greenhouses and Domes: Building greenhouses or domes with controlled environments can protect crops from harsh external conditions while providing optimal growth conditions.
- LED Lighting: Utilizing energy-efficient LED lighting can simulate sunlight and promote photosynthesis, even in low-light environments.
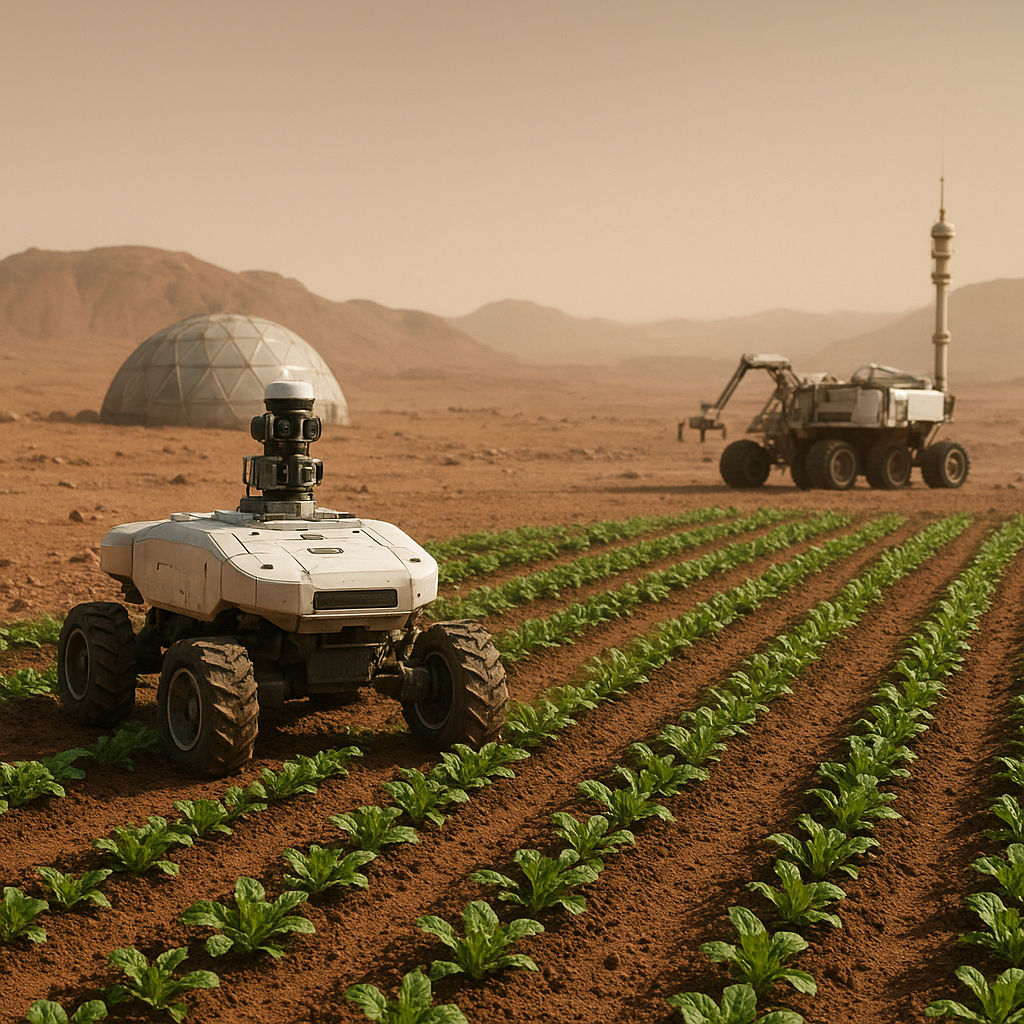
4. Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation will play a crucial role in exoplanetary farming, allowing for efficient planting, monitoring, and harvesting of crops. Autonomous systems can operate in environments that may be hazardous for human workers.
- Robotic Planters: Automated planting systems can ensure precise seed placement and optimal spacing, maximizing crop yields.
- Drones for Monitoring: Drones equipped with sensors can monitor crop health, soil conditions, and environmental factors, providing valuable data for farmers.
The Future of Farming Beyond Earth
The prospect of farming on exoplanets is not merely a theoretical exercise; it represents a critical step in humanity’s journey to becoming a multi-planetary species. As we continue to explore the cosmos, the development of sustainable agricultural practices will be essential for long-term colonization efforts.
1. Collaboration Between Disciplines
To successfully establish farming on exoplanets, collaboration between various scientific disciplines will be necessary. Agronomists, biologists, engineers, and space scientists must work together to develop integrated solutions that address the unique challenges of extraterrestrial agriculture.
2. Ethical Considerations
As we explore the potential for farming on other planets, ethical considerations must also be taken into account. The impact of introducing Earth-based agriculture to alien ecosystems, as well as the rights of potential extraterrestrial life forms, must be carefully considered.
3. Preparing for the Unknown
While we can theorize about the conditions on exoplanets, the reality may present unforeseen challenges. Developing adaptable farming systems that can respond to changing conditions will be crucial for success.
Conclusion
Farming on exoplanets is a complex and multifaceted challenge that requires innovative thinking and interdisciplinary collaboration. As we look to the stars, the development of sustainable agricultural practices will be essential for ensuring humanity’s survival and prosperity beyond Earth. By harnessing technology, genetic engineering, and controlled environment agriculture, we can pave the way for a future where farming is not limited to our home planet but extends to the far reaches of the universe.